Feature Story
Guide to selecting the most suitable Buck for your application
Richtek has a wide range of Step-Down DC/DC (Buck) converters, but selecting the right Buck converter for your application can be a challenge. In this newsletter, you will learn about the different Buck converter types, and which key parameters need to be considered for choosing the optimal part for your application.
Buck converter basics
Buck converters are switch-mode step-down voltage regulators which can provide higher efficiency and more flexibility at high V
IN/V
OUT ratio and high load current compared to a linear voltage regulator. What is the difference between synchronous and non-synchronous Buck converters? How is switching waveform filtered? How does the control loop work to regulate output voltage? Why is internal R
DS(ON) and switching frequency so important? Find out more in the application note.
.png)
Key selection criteria
Voltage and current rating selection
Richtek Buck converters can be divided into 3 main groups to fulfill different application requirements. Richtek LV Buck converters are suitable for running off single cell Li-Ion batteries as well as supplies from 5V rails. The 18V rated HV Buck converters are often used for applications that run from 12V. We also provide parts up to 36V input range for industrial supplies or automotive applications with large input voltage fluctuation.
When considering Buck current rating, the application average current consumption and peak current are two key factors. The application average current will determine the average heat in switching MOSFETs which is related to conduction losses and switching losses. The device maximum rated current and over-current protection level must be considered when checking application peak load current.
.png)
PSM/Forced-PWM selection for light load efficiency consideration
For supply rails that need to be active in low power standby modes, it is desirable to make the Buck converter efficiency at light load as high as possible. Force-PWM Buck converters keep the switching frequency fixed over the entire load range while Pulse Skip Mode (PSM) will reduce switching frequency at light load, thereby improving light load efficiency since the majority of losses at light load are caused by switching loss. Read more to learn about the PSM operation principle and its advantages and drawbacks.
.png)
Switching frequency consideration
Higher switching frequency makes it possible to use smaller inductor and capacitors, and improves the step load behaviour of the converter. However, it also increases switching losses and extends the EMI radiation frequency range. Higher switching frequency can also limit the maximum step-down ratio that can be achieved : The minimum duty-cycle is limited by the converter minimum ON time and the frequency :
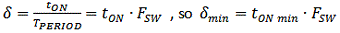
In general, higher V
IN applications should use lower switching frequency devices.
.png)
Lowest BOM cost
Looking for the biggest bang for your Buck? Choosing the right Buck topology together with the most optimal IC package can bring you cost savings on both passive components and IC cost.
ACOT® topology offers superior load transient response, making it possible to reduce the size of your output capacitors and still meet the load transient voltage undershoot requirement.
Flip-Chip in TSOT-23-6 package offers lowest package cost, while maintaining good thermal performance and low R
DS(ON) due to the absence of bonding wires.
.png)